Hypoparathyroidism is a rare disorder in which the body produces too little or no parathyroid hormone. This hormone, together with another hormone called calcitonin and vitamin D regulates the amount of calcium in the blood.
Hypoparathyroidism can result in hypocalcaemia which is an abnormally low level of calcium in the blood.
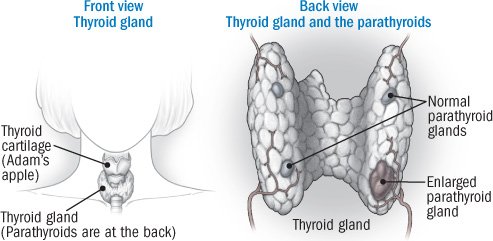
Parathyroid hormone is produced by the parathyroid glands, four small glands located behind the thyroid gland in the neck.
Hypoparathyroidism is either hereditary or acquired.
In hereditary hypoparathyroidism, the parathyroid glands are either absent at birth or fail to function properly for some unknown reason.
Acquired hypoparathyroidism most commonly occurs when the parathyroid glands are removed or damaged during surgery. This form is less common.
Symptoms
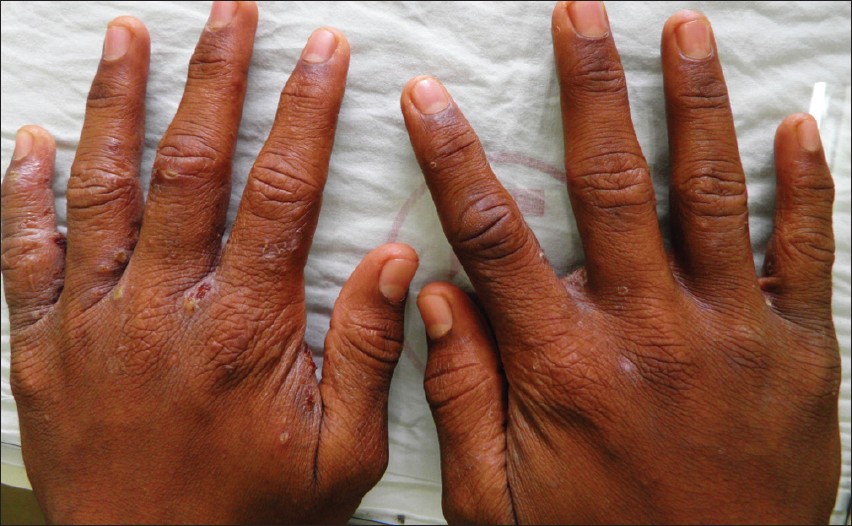
The symptoms are as a result of the low levels of calcium in the body. The most common symptom is tetany which causes twitching and painful spasms in muscles of the face, hands, arms, throat and, sometimes, the feet.
In addition to tetany, symptoms accompanying hereditary hypoparathyroidism include:
- Hair loss
- Dry skin
- Yeast infection
- Poor tooth development in children
- Mental retardation
Prevention/ Treatment

There is no cure for either hereditary or sustained acquired hypoparathyroidism. Treatment is with vitamin D and calcium supplements, to maintain a normal level of calcium in the blood. Vitamin D is necessary because it helps your body to absorb calcium.