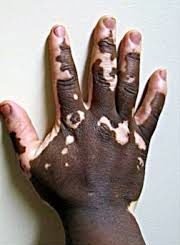
Vitiligo is a condition in where white patches develop on the skin. It can affect any area of the skin, and most people with vitiligo have white patches on the face, neck and hands.
Causes
The condition is as a result of loss of melanin. Melanocytes – the pigment forming cell have been destroyed.
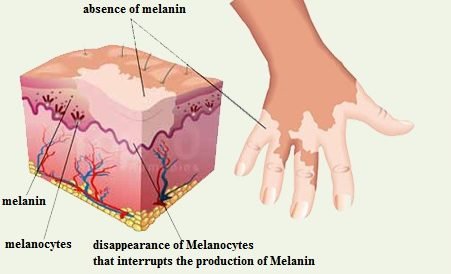
Vitiligo affects all races but is more noticeable in dark skinned persons. It affects about 1% of the global population.
Risk factors
Vitiligo may be hereditary i.e. it runs in the family.
Autoimmune diseases, such as autoimmune thyroid disease (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis) or type 1 diabetes, can also raise your odds.
Symptoms
There is pigment loss in some areas of the skin. Once the white patches appear, they may stay the same for a while, but later on, get bigger.
Vitiligo commonly affects body folds (such as armpits), places that have been injured in the past, and areas exposed to sun, around moles, or around body openings. It can also affect eyelids and hair.
It’s rare for pigment to return once the white patches have developed.
Diagnosis and Treatment

Physical examination of the skin by a Doctor is used to diagnose the condition.
There is no cure or known ways to prevent vitiligo. However it can be managed by improving the appearance of affected skin with cosmetics and corticosteroid creams. Re-pigmentation of the white skin using UV light therapy or lightening the skin in unaffected areas, or a skin graft can also be done.
Tips to manage vitiligo;
Protect your skin from the sun
To protect your skin from the sun, dermatologists recommend that you:
- Use sunscreen every day.
- Wear clothing that protects your skin from the sun.
- Seek shade.
- Do not use tanning beds and sun lamps.
- Add colour to your skin safely. If you want to add colour to your skin, consider using self-tanner, concealing cream, dye, or makeup.
- Do not get a tattoo.










One Response
Thanks for the information.